SLAB DOCUMENTATION
JANUARY 22, 1998
by V.Lee, RPN, AES, Environment Canada
Introduction: What is a slab?
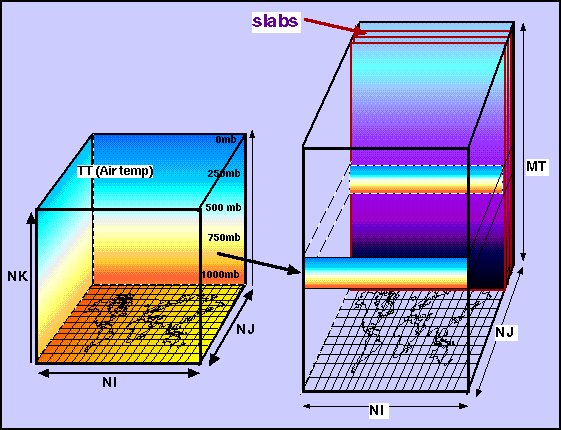
In most of the atmospheric numerical models, a field (ie: TT) is represented by a 3-dimensional grid in which NI by NJ gives the 2-D aspect of the surface of the earth and, NK is the number of vertical levels of the atmosphere. The NI by NJ plane defines the model grid. Each surface field is defined as (NI*NJ) while each profile field is defined as (NI*NJ*NK). A given data set can contain both of these different data sets defined as (NI*NJ*MT) where
MT= # of surface fields + (# of profile fields * NK)
The model integration is usually done in vertical slices (NI*MT) of this cube, incremented along the J axis. One of these vertical slices is what we can call a "slab". You could also take this vertical slice and slice it into multiple columns, making many smaller slabs. Thus, a slab in general is a slice of the model cube where the plane lies on the I and MT axes given one value of J.
Output of data fields during integration.
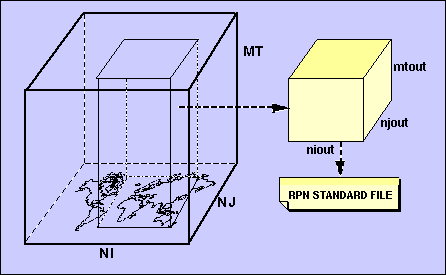
Normally, for a given output timestep, fields requested for output (mtout records) are written out in the specified output grid (niout by njout) once all the vertical slices of the model cube have been completed for that timestep.
Output of data fields during integration using SLAB functions
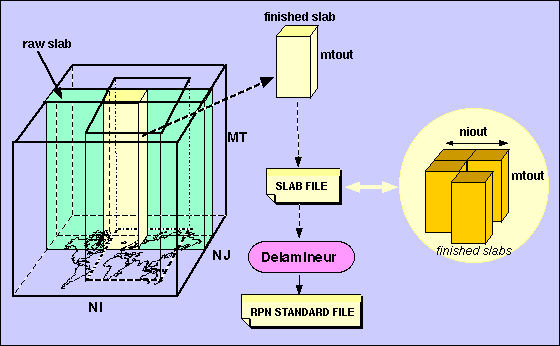
Another way of implementing this would be, as each vertical slice becomes complete for a given output timestep, write the slice (slab) out to an intermediate file (slab file) and continue on with the integration. After the simulation, take the slab file and re-assemble the slabs into the order of the output cube and then, write out the fields in the specified output grid. This would also allow the slices to be written in any order, as long as they are for the same timestep. In fact, a slice could be broken into columns so that one half could be written later than the other half. This technique allows the possibility of processing sections of the model grid by separate computer processors. For example, the model cube can be partitioned on the model grid so that each part can be processed individually by a CPU (parallel processing). As each vertical slice from each of the "sub-cubes" are completed, they can be written to the slab file while their integration continues. The end result is still the same except that there would be more slabs written.
The setup and implementation of writing slices to the slab file is done by using the slab functions. The post-processing of the intermediate file (re-assembly of slabs) is done by using the program Delamineur.
Delamineur
The post-processing program "Delamineur" is used on the slab file afterwards to assemble the slabs into their respective cubes and, write out the output fields in their respective output grids. The final output file is stored in RPN STANDARD file format. Usage:-
delamineur slabfile rpnfile [-f "filter numbers"]
slabfile - input filename of the slab file
rpnfile - output filename of the resulting RPN standard file
filter numbers - filter numbers to be used for filtering in the re-assembly process
-
delamineur slabfile2 stdfile2 -f "1 0 1"
The Slab Functions
The slab functions will take the given vertical slices (raw slabs), reduce them down to only the information required for final output, and write out these refined vertical slices (finished slabs) into the slab file. The finished slabs actually contain only the requested fields and the grid points that cover the specific output grid area. The slab file can have more than one type of finished slabs, each classified by a slab id that associates it to a defined output grid and a list of the requested fields for output. With each slab id, the necessary information to re-construct the fields at a later time on the output grid is also stored in the slab file. These defined output grids must be a subset of the model grid. The order of the assorted finished slabs written into the slab file is not important as long as, all the slabs needed to cover each defined output grid area are present.
The user needs four functions in order to create and save the slab files. The SLABINI function initializes and opens a "slab file". The SLABEND function closes a "slab file". The SLABDSC function describes a slab type given the output grid and the description of the fields that will be extracted for this grid. During integration of the model, the SLABXTR function takes a given vertical slice (raw slab), extracts only the fields to be outputted within the region of the output grid, scales these output fields and writes them as a block (finished slab) into the slab file. The details on how to use each of these functions are described later on or just click on the links of each function.
In order to use these functions, you must link them to the compiled slab functions as follows:
Server:
-
f77 main.f $ARMNLIB/lib/write_slab32stack.o $ARMNLIB/lib/librmnx32stack.a
-
f7732 main.f $ARMNLIB/lib/write_slab32multi.o $ARMNLIB/lib/librmnx32stack.a
-
f7764 main.f $ARMNLIB/lib/write_slab64multi.o $ARMNLIB/lib/librmnx64stack.a
Usage:
-
f_hand = slabini(f_name, dateo, npas, deet, etiket)
Function:
-
To initialize and open a file [f_name] to contain slabs and to save a few general parameters needed to describe all the slabs. This routine returns the file handler [f_hand] associated to this file.
Arguments:
|
I/O |
Parameter |
Format |
Description |
|
IN |
f_name |
character*128 |
filename of slab file |
|
IN |
dateo |
integer(2) |
date and time of origin of the data where: dateo(1)=YYYYMMDD and dateo(2)=HHMMSShh |
|
IN |
npas |
integer |
model timestep number for output |
|
IN |
deet |
integer |
length of model timestep in seconds |
|
IN |
etiket |
character*9 |
label (type of run, numerical model...) |
|
OUT |
f_hand |
integer |
file handler of the initialized slab file |
Usage:
-
ier = slabdsc(f_hand, snum, gxtyp, ixyg1, ixyg2, ixyg3, ixyg4,
niout, njout, nxgrid, nygrid, xgrid, ygrid, grtyp, ig1, ig2, ig3, ig4,
mtout, np, typvar, nomvar, ip1, ip2, ip3, datyp, nbits, iflt, xp)
Function:
-
To define one type of slab associated to slab index snum. This includes the parameters of the output grid which must be a subset
of the model grid and the description of each record stored in the
finished slab (ie: variable name, forecast hour, vertical level, etc).
It returns a value of zero if no error
Arguments:
|
I/O |
Parameter |
Format |
Description |
|
IN |
f_hand |
integer |
file handler of the initialized slab file. |
|
IN |
snum |
integer |
index for type of slab(slab id). You can have more than one type of slab in a slab file. 0 >= snum < 10 |
|
IN |
gxtyp |
character*4 |
grid type for the positional (>> and ^^) records (ie: L,N,S,..) |
|
IN |
ixyg1 |
integer |
grid descriptor 1 in ig1 field of the positional (>> and ^^) records |
|
IN |
ixyg2 |
integer |
grid descriptor 2 in ig2 field of the positional (>> and ^^) records |
|
IN |
ixyg3 |
integer |
grid descriptor 3 in ig3 field of the positional (>> and ^^)records |
|
IN |
ixyg4 |
integer |
grid descriptor 4 in ig4 field of the positional (>> and ^^)records |
|
IN |
niout |
integer |
(<=NI) X dimension of the output grid |
|
IN |
njout |
integer |
(<=NJ) Y dimension of the output grid |
|
IN |
nxgrid |
integer |
dimension of xgrid (= niout or niout+1 for Z grid, = niout*njout for Y grid) |
|
IN |
nygrid |
integer |
dimension of ygrid (= njout for Z grid, = niout*njout for Y grid) |
|
IN |
xgrid |
real(nxgrid) |
">>" positional record |
|
IN |
ygrid |
real(nygrid) |
"^^" positional record |
|
IN |
grtyp |
character*4 |
grid type for each record except the positional records (ie: L,N,S,E,G,Y,Z..) |
|
IN |
ig1 |
integer |
grid descriptor 1 or =ip1 of positional records if grtyp='Y' or 'Z' |
|
IN |
ig2 |
integer |
grid descriptor 2 or =ip2 of positional records if grtyp='Y' or 'Z' |
|
IN |
ig3 |
integer |
grid descriptor 3 or =ip3 of positional records if grtyp='Y' or 'Z' |
|
IN |
ig4 |
integer |
grid descriptor 4 |
|
IN |
mtout |
integer |
total number of records in the finished slab excluding the positional records (total number of fields for output in this slab id) |
|
IN |
np |
integer |
2nd dimension of field xp |
|
IN |
typvar |
character*1(mtout) |
type of data field for each record (ie: 'P','A') |
|
IN |
nomvar |
character*4(mtout) |
name of variable for each record (ie: 'TT','UU') |
|
IN |
ip1 |
integer(mtout) |
vertical level in sigma,pressure or height for each data record |
|
IN |
ip2 |
integer(mtout) |
forecast hour for each data record (ie: 0,3,12,24,48) |
|
IN |
ip3 |
integer(mtout) |
optional descriptor for each data record (useful to distinguish records if they already have the same nomvar,etiket,ip1,ip2,date in the same file) |
|
IN |
datyp |
integer(mtout) |
type of data
|
|
IN |
nbits |
integer(mtout) |
number of bits kept for the data fields (ie: 12,16,24) |
|
IN |
iflt |
integer(mtout) |
number of filter passes for each data record |
|
IN |
xp |
real(mtout,np) |
information added to each record (optional) |
|
OUT |
ier |
integer |
value returned by function; non-zero value indicates an error |
Usage:
-
ier = slabxtr(f_hand, snum, nx, xnio, mt, mtas, mtadd, mtmul, mtval)
Function:
-
For a given slab type (snum), take a vertical slice (raw slab) mtval(nx,mt) from the model cube, extract only the rows and columns needed to make the finished slab and, then write it into the slab file (f_hand). The rows to be extracted are determined in mtas(mt) while the columns to be extracted are determined in xnio(nx). Before the finished slab is written to the slab file, each point extracted from mtval(i,k) is multiplied by their respective mtmul(k) and then added by their respective mtadd(k). See diagram below.
Arguments:
|
I/O |
Parameter |
Format |
Description |
|
IN |
f_hand |
integer |
file handler of the slab file |
|
IN |
snum |
integer |
slab identification number (slab id) |
|
IN |
nx |
integer |
(<=ni)dimension of xnio and 1st dimension of mtval |
|
IN |
xnio |
integer(nx) |
indicator of which points are to be extracted for the output grid. If positive, it will give the row and column position in the output grid by the formula: xnio(i) = i + j*niout where j = current slice # and 1<=i<=nx. If zero, no extraction for this grid point. |
|
IN |
mt |
integer |
the total number of records in the given raw slab |
|
IN |
mtas |
integer(mt) |
output indicators for each record in raw slab. (1) to output, (0) to not output to finished slab. |
|
IN |
mtadd |
real(mt) |
value to add to the data field of each record if indicated for output. (must be multiplied by mtmul first) |
|
IN |
mtmul |
real(mt) |
value to multiply to the data field of each record if indicated for output. (see mtadd) |
|
IN |
mtval |
real(nx,mt) |
the input raw slab from the model cube. |
|
OUT |
ier |
integer |
value returned by function; non-zero value indicates an error |
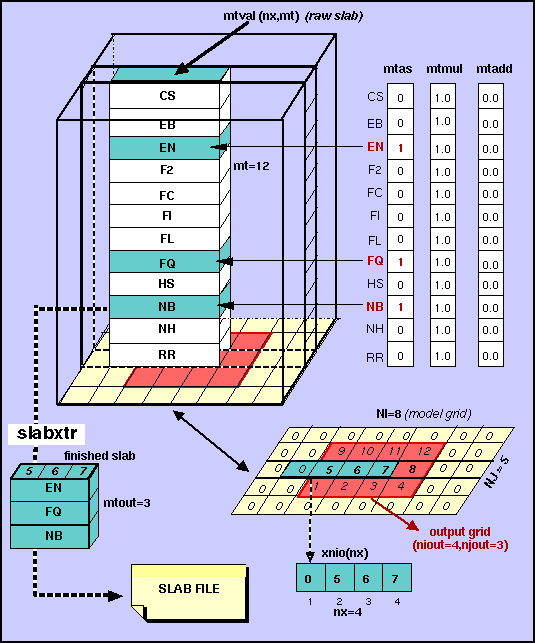
Usage:
-
ier = slabend(f_hand, sf_end)
Function:
-
To put an indicator for end of slab file and close the slab file.
Arguments:
|
I/O |
Parameter |
Format |
Description |
|
IN |
f_hand |
integer |
file handler of the slab file |
|
IN |
sf_end |
character*4 |
slab file end indicator 'SLB9' |
|
OUT |
ier |
integer |
value returned by function; non-zero value indicates an error |
Example Program
#!/bin/sh # programme=$TMPDIR/program.f action=action$$ # \rm final.fst \rm slabfile1 \rm stdfile1 cat <${programme} PROGRAM SLABTEST4 * IMPLICIT NONE * INTEGER I,J,K,N,NI,NJ,NK,INBR INTEGER MTL,MTLO INTEGER NIL,NJL INTEGER NIL2 INTEGER NJL2 INTEGER NXGRIDL,NYGRIDL * latlon grid for Wave Model PARAMETER (NIL=66,NJL=46) PARAMETER (NXGRIDL=NIL,NYGRIDL=NJL) PARAMETER (NIL2=33,NJL2=23) PARAMETER (MTL=16,MTLO=16) * REAL l(NIL,NJL),m(NIL2,NJL2) REAL xpl(MTL) REAL cubel(NIL,NJL,MTL) REAL slabl(NIL,MTL) REAL xlat0,xlon0,dlat,dlon integer xniol(NIL,NJL,2) character *4 sf_end data sf_end/'SLB9'/ integer mtasl(MTL) data mtasl/1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1/ real mtmull(MTL) data mtmull/1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0, + 1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0/ real mtaddl(MTL) data mtaddl/0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0, + 0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0/ character*4 nomvarl(MTL) data nomvarl/'WH','UV','WD','MP','PD','SZ','DS','DE', + 'SQ','UU','VV','WU','WV','WX','WY','WZ'/ integer ipp1l(MTL) data ipp1l/0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0/ character*4 nvarl(MTLO) integer ip1l(MTLO),ip2l(MTLO),ip3l(MTLO),datypl(MTLO) integer ip3ll(MTLO) character*1 typvarl(MTLO) integer nbitl(MTLO) integer ifltl(MTLO) REAL xgridl(NXGRIDL),ygridl(NYGRIDL) * integer dateo,datyp,deet,nbits,npas integer ippl integer s_dateo(2) data ippl/24/ integer ip1,ip2,ip3,ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4,iprm integer n_ig1,n_ig2,n_ig3,n_ig4 integer swa,lng,ubc,dltf,extra1,extra2,extra3 * integer xg1,xg2,xg3,xg4 * character grtyp*4,gxtyp*4,typvar*1,nom*2 character s_etiket*8,etiket*8 * * integer f_hand2,ier INTEGER FSTFRM, FSTOUV, FSTLIR, FSTVOI EXTERNAL FSTFRM, FSTOUV, FSTLIR ,FSTVOI,CIGAXG,CXGAIG INTEGER FSTPRM, FSTECR, FNOM, FCLOS, NEWDATE EXTERNAL FSTPRM, FSTECR, FNOM, FCLOS, NEWDATE INTEGER SLABINI, SLABDSC, SLABXTR, SLABEND EXTERNAL SLABINI, SLABDSC, SLABXTR, SLABEND * * - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - * INBR = FNOM ( 20 , '1998010700_024', 'STD+RND' , 0 ) INBR = FNOM ( 30 , 'final.fst', 'STD+RND' , 0 ) * * INBR = FSTOUV (20, 'RND') INBR = FSTOUV (30, 'RND') * J=0 DO 15 I=1,MTL if (mtasl(i).ne.0) then j = j+1 nvarl(j)=nomvarl(i) ip1l(j)=ipp1l(i) endif 15 CONTINUE * initialization of MTL variables DO 20 I=1,MTLO typvarl(i)='P' datypl(i)=1 nbitl(i)=16 ifltl(i)=4 xpl(i)=0.0 ip2l(i)=ippl ip3l(i)=0 ip3ll(i)=1 20 CONTINUE * Define XNIO's * xniol(i,j,1) extracts the whole LL grid(L) (NIL*NJL) * xniol(i,j,2) extracts every second point (NIL*NJL)from the L grid(L) * to give L grid (S) * * DO 40 J=1,NJL DO 35 I=1,NIL xniol(i,j,1)= i + (j-1)*NIL xniol(i,j,2)=0 35 CONTINUE 40 CONTINUE DO 50 J=1,NJL2 DO 45 I=1,NIL2 xniol(i*2 -1,j*2 -1,2)= i + (j-1)*NIL2 45 CONTINUE 50 CONTINUE gxtyp=grtyp xg1=ig1 xg2=ig2 xg3=ig3 xg4=ig4 * * read the variable grid L records and fill in the cubel DO 115 I=1,MTL INBR = FSTLIR(cubel(1,1,I),20,NI,NJ,NK,-1,' ',ipp1l(i), + ippl,-1,' ',nomvarl(i)) 115 CONTINUE * get information from these records iprm = fstprm(inbr,DATEO,DEET,NPAS,NI,NJ,NK,NBITS, + DATYP,IP1,IP2,IP3,TYPVAR,NOM,ETIKET, + GRTYP,IG1,IG2,IG3,IG4,SWA,LNG,DLTF,UBC, + EXTRA1,EXTRA2,EXTRA3) * get the date,time ier = newdate(dateo,s_dateo(1),s_dateo(2),-3) * initialization of the slab file s_etiket=etiket f_hand2 = slabini('slabfile1',s_dateo,npas,deet,s_etiket) print *,'f_hand2=',f_hand2 * description of slab 2+3 (for variable grid L NIL*NJL) print *,'BEFORE slabdsc for slab1' print *,'gxtyp=',gxtyp,'grtyp=',grtyp print *,'xg1,xg2,xg3,xg4=',xg1,xg2,xg3,xg4 print *,'nio,njo,NXGRIDL,NYGRIDL=',NIL,NJL,NXGRIDL,NYGRIDL print *,'ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4=',ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4 print *,'mt_nrows=',MTLO print *,'ip1=',ip1l print *,'ip2=',ip2l print *,'ip3=',ip3l print *,'ip3ll=',ip3ll print *,'typvar=',typvarl print *,'nvar=',nvarl print *,'datyp=',datypl print *,'nbit=',nbitl print *,'iflt=',ifltl write(6,*)'IG1,IG2,IG3,IG4=',ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4 CALL CIGAXG(grtyp,XLAT0,XLON0,DLAT,DLON,ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4) write(6,*)'XLAT0,XLON0,DLAT,DLON=',XLAT0,XLON0,DLAT,DLON CALL CXGAIG(grtyp,N_IG1,N_IG2,N_IG3,N_IG4,xlat0, + xlon0,dlat*2.0,dlon*2.0) write(6,*)'new IG1,IG2,IG3,IG4=',n_ig1,n_ig2,n_ig3,n_ig4 * latlon grid ier=slabdsc(f_hand2,1,gxtyp,xg1,xg2,xg3,xg4,NIL,NJL, + NXGRIDL,NYGRIDL, + xgridl,ygridl,grtyp,ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4,MTLO,0, + typvarl,nvarl,ip1l,ip2l,ip3l,datypl,nbitl,ifltl,xpl) * same latlon grid but every second point ier=slabdsc(f_hand2,2,gxtyp,xg1,xg2,xg3,xg4,NIL2,NJL2, + NXGRIDL,NYGRIDL, + xgridl,ygridl,grtyp,n_ig1,n_ig2,n_ig3,n_ig4,MTLO,0, + typvarl,nvarl,ip1l,ip2l,ip3ll,datypl,nbitl,ifltl,xpl) * writeout NIL*NJL L records to RPN standard file n=1 DO 130 K=1,MTL IF (mtasl(k).eq.1) THEN DO 125 J=1,NJL DO 120 I=1,NIL l(i,j)=cubel(i,j,k)*mtmull(k) + mtaddl(k) 120 CONTINUE 125 CONTINUE ier = fstecr(l,l,-1*nbitl(n),30,dateo,deet,npas,NIL,NJL, + 1,ip1l(n),ip2l(n),ip3l(n),typvarl(n),nvarl(n),s_etiket, + grtyp,ig1,ig2,ig3,ig4,datypl(n),.false.) n = n+1 ENDIF 130 CONTINUE n=1 DO 150 K=1,MTL IF (mtasl(k).eq.1) THEN DO 140 J=1,NJL2 DO 135 I=1,NIL2 m(i,j)=cubel(i*2-1,j*2-1,k)*mtmull(k)+mtaddl(k) 135 CONTINUE 140 CONTINUE ier = fstecr(m,m,-1*nbitl(n),30,dateo,deet,npas,NIL2,NJL2, + 1,ip1l(n),ip2l(n),ip3ll(n),typvarl(n),nvarl(n),"HALF", + grtyp,n_ig1,n_ig2,n_ig3,n_ig4,datypl(n),.false.) n = n+1 ENDIF 150 CONTINUE print *,'slabxtr for slab2 and slab3' DO 250 J=1,NJL DO 240 K=1,MTL DO 230 I=1,NIL slabl(i,k)=cubel(i,j,k) 230 CONTINUE 240 CONTINUE ier=slabxtr(f_hand2,1,NIL,xniol(1,J,1),MTL,mtasl, + mtaddl,mtmull,slabl) ier=slabxtr(f_hand2,2,NIL,xniol(1,J,2),MTL,mtasl, + mtaddl,mtmull,slabl) 250 CONTINUE * ier=slabend(f_hand2,sf_end) * INBR = FSTFRM (20) INBR = FSTFRM (30) CALL FCLOS(20) CALL FCLOS(30) * STOP END FIN.DE.PROGRAMME # # f77 ${programme} write_slab.o ${ARMNLIB}/lib/librmnx32stack.a -o ${action} ${action} # \rm ${action} ${programme} program.o #